Roofing Terms
Know the basics of roofing with these terms.
Whether you choose to hire a contractor or DIY, it's important to know your way around a roof and understand the different parts of your roofing system. Below are some common roofing terms:
a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
Barge rafter: Typically a 2×6 or larger dimension board used at the edge of a roof. The wood used is usually Hem Fir or Spruce. Some customers choose to pre-paint this wood because it is easier to paint these boards on sawhorse on the ground than it is to paint up on a ladder. Below contractors are removing an old dry rotten barge rafter and are replacing it with a new pre-painted one. The best time to do this work is during the re-roofing process.
Bleeder: A strip of asphalt material along with the rake over an unseen drip edge metal. The bleeder strip here is along with the rake under the asphalt shingles. It creates a nice straight look from the ground looking up and adds another layer of protection in the roofing system. Here a 9-inch roll was used.
Burnout: The term where felt (tar paper) has had UV rays deteriorate the roofing and burn a hole through it. This is seen on cedar shake roofs when a cedar shake has split or worn away leaving the felt exposed and soon after that the sun burns a hole through the felt.
Compo: A composition shingle made of asphalt and fiberglass mat with ceramic coated granules embedded on the surface. Superior products have reinforcement weave also in the asphalt to ensure a high-performance shingle.
Class A, B or C Fire Rating: A classification is given by laboratories that test roofing products for fire ratings. Most asphalt shingles and tile roofs have a Class A rating, which is the most fire resistant. Metal roofs can achieve a Class A or B rating. Cedar shakes typically have a Class C rating, which is the least fire resistant, but can also achieve a Class A or B rating.
Cricket: An area behind a chimney or wall that has a slope designed to move water away and down the roof.
Deflection: As seen on this old garage, deflection is the sagging of the roof framing. This normally is caused by poorly installed solar ties or wall joists. The rafter pushes out the walls at the top plate as the weight of the roof squats downwards.
Diverter: This metal strip serves as a water diversion to move the water on the roof away from an opening where gutters cannot be installed. This metal is 12 x 2-inch high x 10 feet long. The 12 inch part is installed under the shingles and must be maintained if you have trees near the home, but is a great way to keep water dumping into this open area.
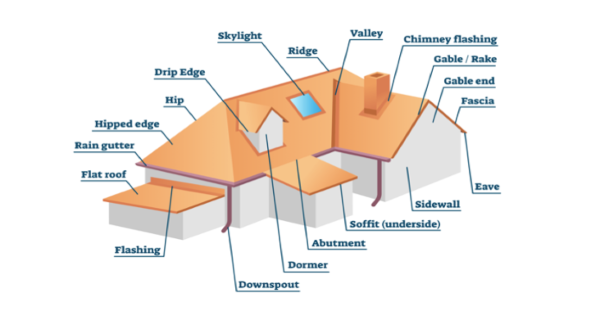
Dormer: A small gable or shed roof in the middle of a larger roof. See diagram.
Dormer vent: A sheet metal exhaust vent installed on top of the roof to ventilate the attic. This should be installed no lower than three feet from the ridge.
Double felt: Double felting a deck is typically done on low sloped roofs under 4 and 12 pitch where the roofing is to be applied. Here is an example of a 3.5/12 pitch front porch having a first ply of 30/36 felt then the shake liner at 10-inch exposure for cedar shake application. Once up past the porch the roof becomes 4/12 pitch and the double felting is not required over the skip sheathing.
Downspout: The vertical trough that is connected to the gutter to assist with removing water from the roof and gutters. See diagram.
Dry rot: Deterioration of wood fibers caused by moisture intrusion for a long period. Many times dry rot on the roof can go undiscovered for years.
Dutch gable: A combination of a hip style roof and a gable.
Eave: The area of the roof that overhangs the lower edge. See diagram.
Eave vents: Small screens under the eave that allow fresh air to enter the attic.
Exposure: This term is used for the area of roofing material that is exposed to the weather. This is one of Bob's many old photos in his collection. Notice the shingle is 18 inches long, tucking under 3 courses but the exposure is only 4-1/2 inches.
Fascia: Pronounced fay-sha, it is the horizontal board attached to the eaves rafter tails.
Felt: This is sometimes called "tar paper" and is a moisture barrier to protect the roof deck. This is used in most roofing systems.
Fiber cement shakes/slate: A class A roofing material designed to look like shakes made with Portland lightweight cement and wood fibers.
Flashing: A corrosion-resistant metal designed to terminate roofing at walls, chimneys or penetrations through the roof. Before it was painted, the bare metal would glare and flash sunlight in the eyes of the roofers, which is how it got its name.
Gable: The triangular roof shape at the end of a building, as seen here. See diagram.
Gutters: Rain gutters are attached to the eave of the roof and catch rainwater, controlling the roof drainage runoff. Many homeowners are very pleased to have pre-painted seamless gutters because it adds a fresh look to accompany their new roof. Traditional gutters come in 7 1/4″ & 5 1/2″ fascia and the 5 1/2″ OGEE style gutters in brown and white baked-on enamel for a long life outside & inside the gutter.
Hip: The convex junction of two adjacent roof plains. See diagram.
Joist: A ceiling is nailed to this framing members. These are also used to tie walls together.
Loading: Delivering the roofing material from the street to the rooftop by conveyor. Loading the roof is the term for the delivery of materials to the rooftop. This can be done with a lift bed truck or a large conveyor as seen here. Most companies use local distributors that keep a wide variety of roofing products.
Modified bitumen: Low sloped roofing products sold in rolls usually applied with a torch. It is a single-ply system with very good durability. A base sheet is attached to the roof deck, then the modified bitumen is applied to the base sheet using a torch to melt the material, which seals all the edges and laps.
Nosing or drip edge: The pre-fold edge metal installed along the eaves and rakes of the roof.
Outrigger: 2″ x 4″ framing to support a barge rafter, here seen unpainted. This is also called look outs.
OSB: An alternative to plywood used for roof decking. Oriented Strand Board is made from wood chips oriented and glued in layers. It is heavier than plywood because there are no voids. This makes a great roof deck because of its density and sheer value.
Pitch: The slope of a roof. The term three and twelve means three inches of rising in a twelve-inch span.
Plywood: Sheets of thin flat wood laminated together into four by eight-foot sheets used for roof decking.
Purlin: A brace placed in the attic to support the rafters.
Rake: The edge of a gable. See diagram.
Rafter: The framework the roof decking is nailed to.
Roof Jack: A corrosion-resistant metal covering that seals penetrations on the roof such as exhaust fans, gas water heater pipes, and plumbing venting through the roof.
Sidewall: Shinglers use this word for a wall with cedar shingles applied to it. For years cedar shingles have served as a great exterior wall covering giving home's some charm, like the home below with custom diamond-cut shingles and bent corners.
Skip sheeting: Typically 1 x 4’s spaced sheathing is used when cedar shakes and shingles are installed so they can breathe. Shakes are 24 inches applied here at 10 inches to weather and must have felt paper interlaced with the shakes. Cedar shingles are thinner and 18 inches. Exposure here is 5 inches and originally would not use felt since the layout is tripled.
Solar brackets: A hidden bracket that is attached to the roof without putting holes in your new roofing system.
Solid sheeting: This term is for describing a solid deck that has timbers with no gaps, plywood or OSB on it.
A Square: The term square is used as a roofing measurement. 100 square feet, or ten by ten, equals a square. The average home is about 28 squares.
Step shingles: A corrosion-resistant piece of metal that is bent to a 90-degree angle weaved into the shingles at walls, skylights and chimneys.
Tar and gravel: 3-plies of roofing material hot-mopped in layers to the roof deck primarily on low sloped roofs below 2 and 12. This is covered with gravel to protect the roof material from UV sun rays.
Tile - clay or concrete: A type of roofing material. Featured here are a concrete tile and clay mission style cap and pan.
Turbine: This is some times called a whirly-bird and is used to exhaust hot attic air.
Underlayment: The deck of a roof is typically protected by underlayment or what the roofing industry calls felt. It is an asphalt product that is used as a moisture barrier and is used with almost all types of roofing systems.
Valley: Junction where two roof plains meet and water flows down. See diagram. There are many different ways to install valleys with the various roofing products available. Here is a picture of a 14:12 heavy shake with a roof valley. It is installed with 24-inch wide, prepainted, W valley metal. It's called W valley because it is formed in the shape of a W. Before installation a 36-inch-wide felt was laid under the valley metal. The cedar shakes are angle cut to fit, which leaves a trough for water to run down. This type of system will protect the roof deck from moisture intrusion when properly installed.
Ventilation: The term is used to describe the system that provides movement of fresh air into and out of the attic.
Z-bar: This is a termination bar that step shingles are designed to slip under. This is used so siding, or stucco in the picture below, can be separate from the roofing system. This is ideal when a re-roof is done because there is no need to disturb the existing wall covering to change the step flashings.
Have a question? AskARoofer.
Find your local roofing contractor in the RoofersCoffeeShop® Contractor Directory.







